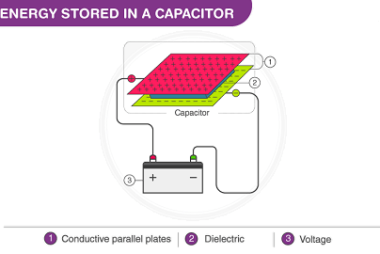
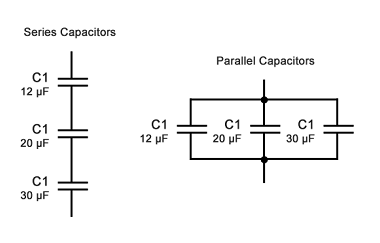
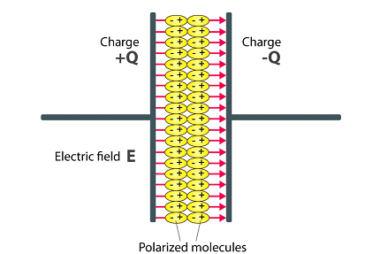
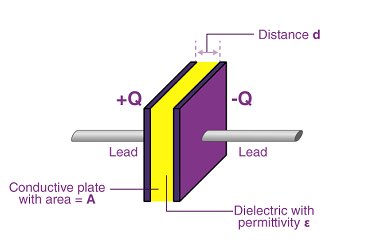
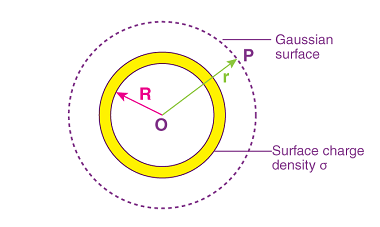
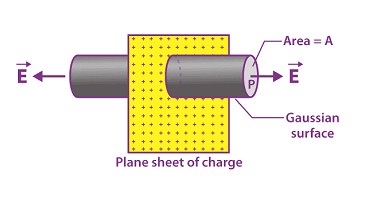
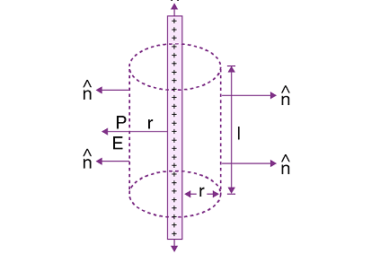
Electric current
Electric current refers to the flow of electric charge in a conductor or circuit. It is the rate at which electric charges, typically electrons, move through a material. The unit of electric current is the ampere (A), which is defined as the flow of one coulomb of charge per second. Electric current can be either…