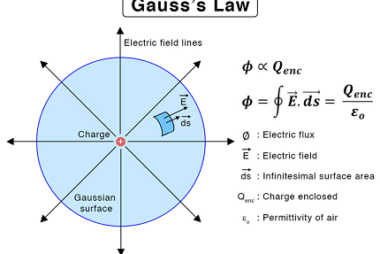
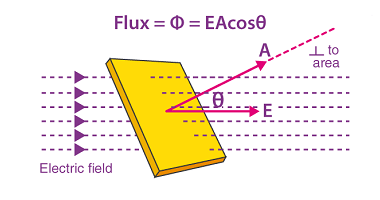
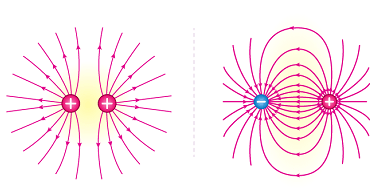
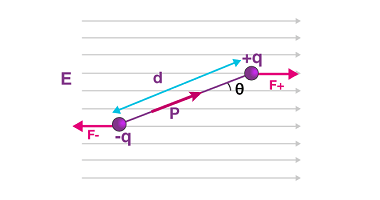
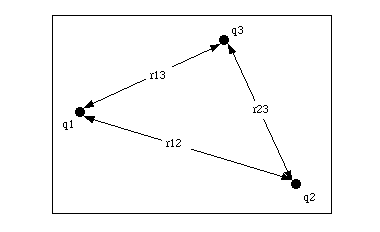
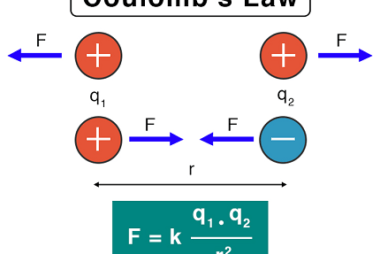
Its application in simple cases
Here are some examples of applications in simple cases: These are just a few examples of the many applications that can be considered “simple” in their functionality. What is Required Its application in simple cases To develop an application for simple cases, you would need to have a basic understanding of programming languages such as…