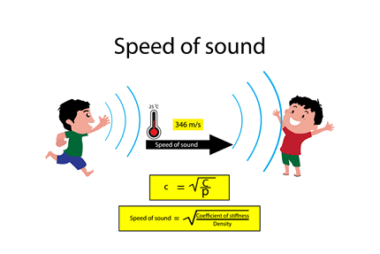
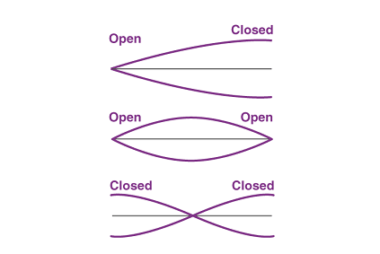
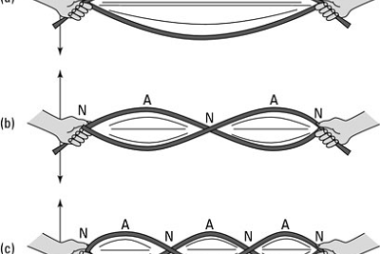
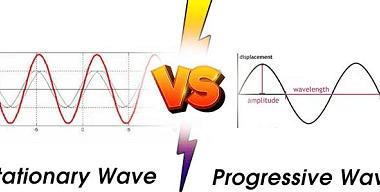
latent heat
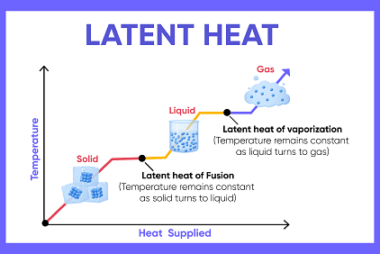
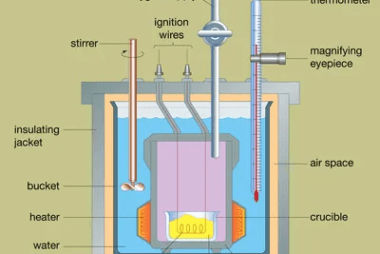
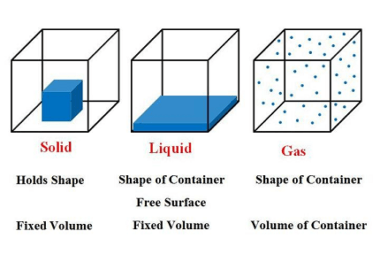
Latent heat refers to the amount of energy that is absorbed or released by a substance during a change in its state or phase, such as melting, boiling, or condensation. This energy is used to either break or form the intermolecular bonds between the molecules of the substance, without causing a temperature change. The amount…