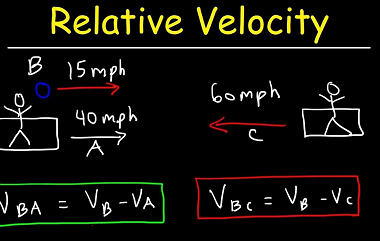
Relative velocity
Relative velocity refers to the velocity of an object with respect to another object. It is the difference between the velocity of the first object and the velocity of the second object, both measured with respect to the same frame of reference. For example, if a car is moving with a velocity of 60 km/h…