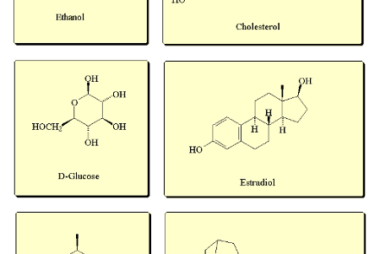
Least Count
Least count is the smallest measurement that can be read and recorded by a measuring instrument. It is a significant term in metrology, which is the science of measurement. The least count of a measuring instrument is determined by its smallest scale division. For example, the least count of a ruler with markings in millimeters…