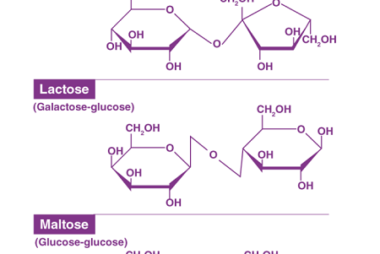
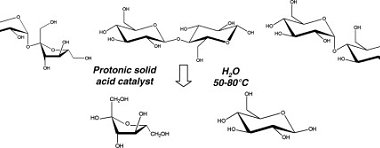
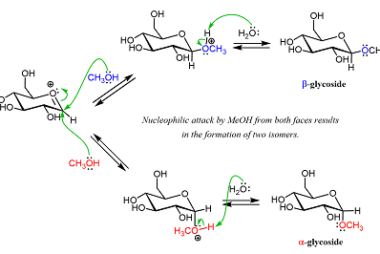
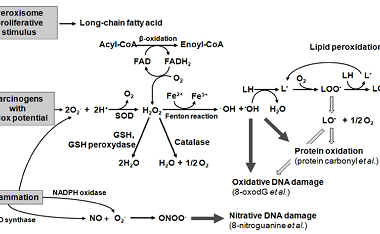
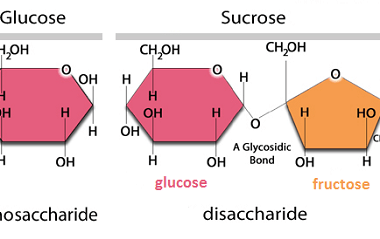
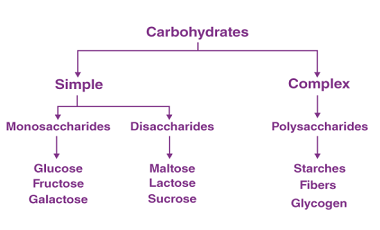
Sucrose, Maltose, Lactose
Sucrose, maltose, and lactose are all types of sugars. Sucrose is a disaccharide made up of glucose and fructose molecules. It is commonly found in table sugar, as well as in fruits, vegetables, and some grains. Maltose is also a disaccharide, but it is made up of two glucose molecules. It is commonly found in…