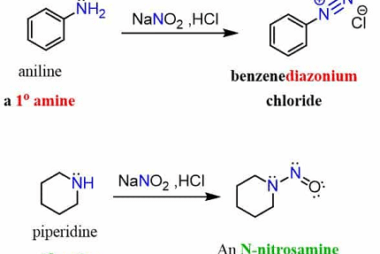
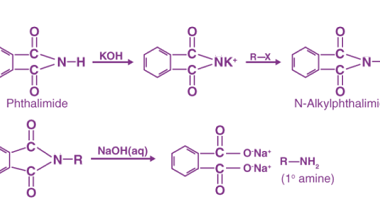
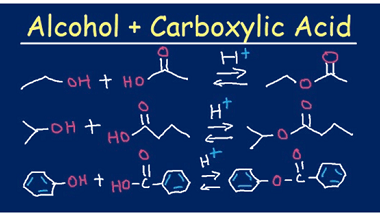
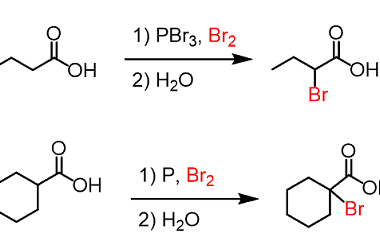
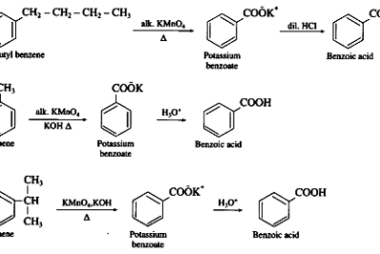
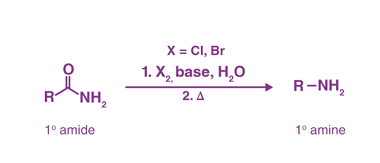Reaction with nitrous acid
The reaction with nitrous acid (HNO2) depends on the conditions and the nature of the compound with which it reacts. In general, nitrous acid is a weak acid and a good oxidizing agent. Here are a few examples of reactions with nitrous acid: CH3CH2OH + HNO2 → CH3CH2ONO C6H5NH2 + HNO2 → C6H5N2Cl + 2H2O…