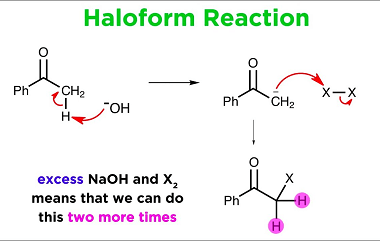
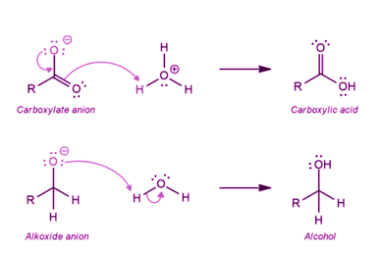
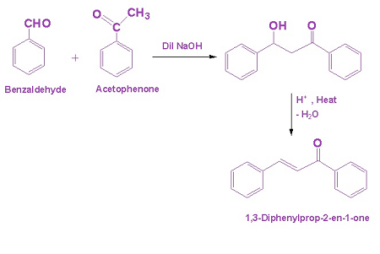
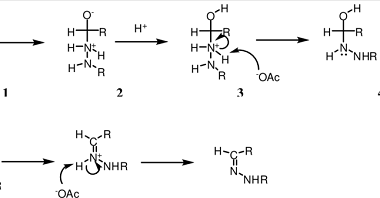
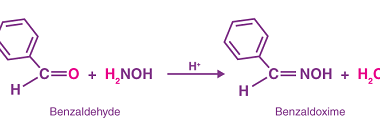
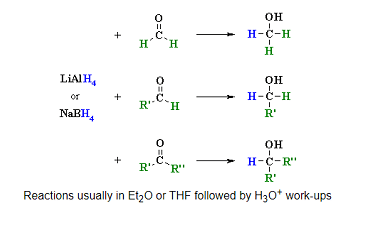
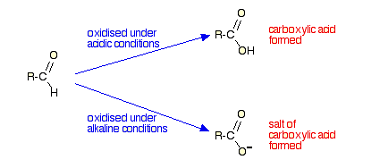
Haloform reaction
The haloform reaction is a chemical reaction in which a methyl ketone (a compound containing a carbonyl group, C=O, bonded to a methyl group, CH3) is treated with a halogen (chlorine, bromine, or iodine) and a strong base (usually sodium hydroxide, NaOH) to produce a carboxylic acid and a haloform (a compound containing a halogen…