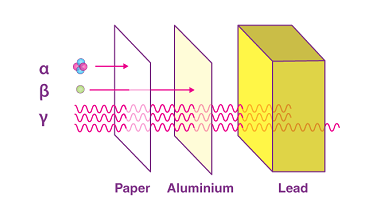
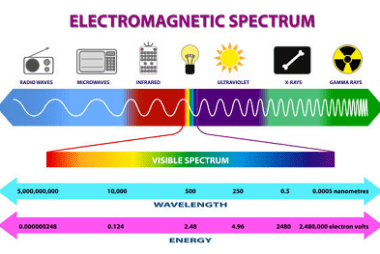
Law of radioactive decay
The law of radioactive decay is a fundamental principle of nuclear physics that describes the process by which unstable atomic nuclei spontaneously emit radiation and transform into more stable nuclei. This process is known as radioactive decay. The law of radioactive decay states that the rate of decay of a radioactive substance is proportional to…