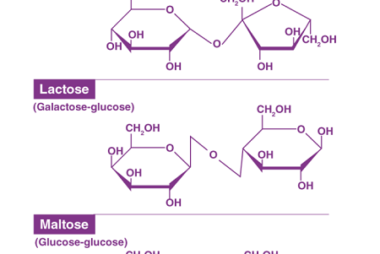
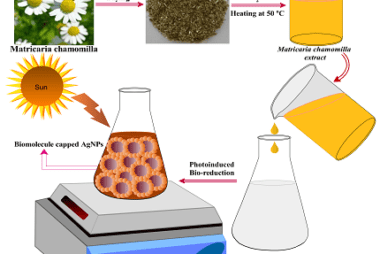
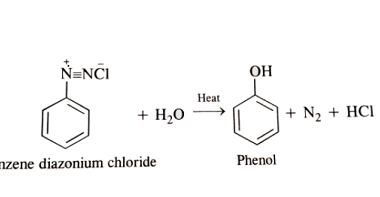
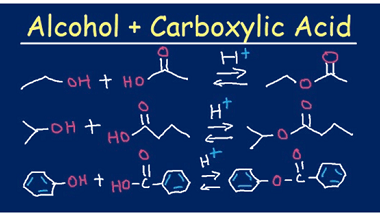
Proteins: Amino acids
Proteins are complex molecules that are essential to life. They are made up of long chains of smaller molecules called amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids that can be combined in various ways to form different proteins. Each amino acid has a unique chemical structure and properties that determine its role in protein…