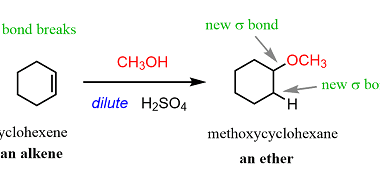
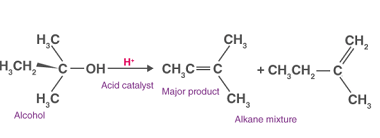
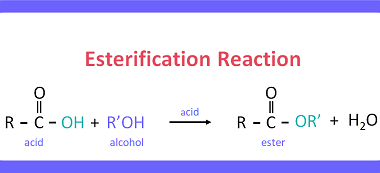
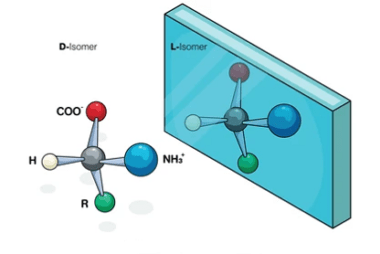
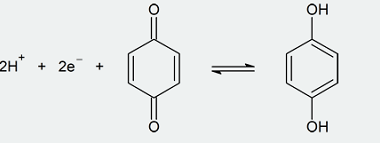
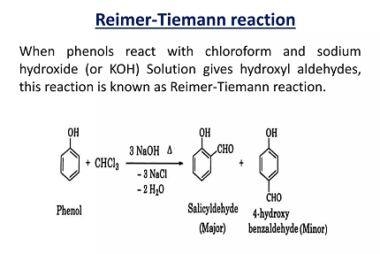
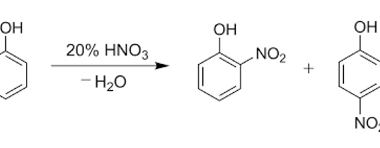
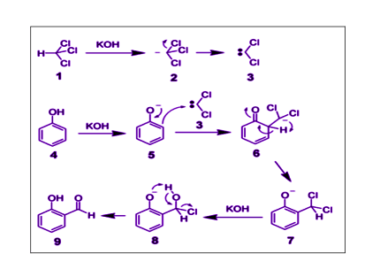
ZnCl2/Concentrated HCl
ZnCl2 is the chemical formula for zinc chloride, and HCl is the chemical formula for hydrochloric acid. When these two substances are combined, they react to form a complex mixture of products. The reaction between ZnCl2 and HCl is exothermic, meaning that it releases heat as it proceeds. The products of the reaction include hydrogen…