Group 17 Oxoacids of halogens
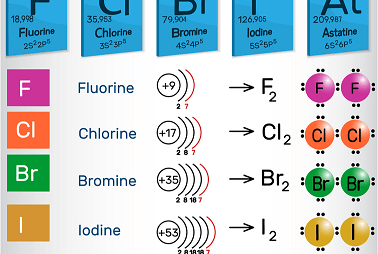
The Group 17 halogens, also known as the halides, form a series of oxoacids with varying numbers of oxygen atoms. The oxoacids of the halogens are named based on the number of oxygen atoms in the molecule and the oxidation state of the halogen. Here are the oxoacids of the halogens: The oxoacids of the…