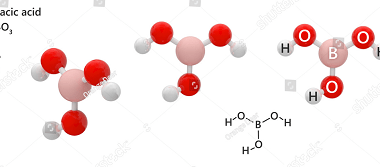
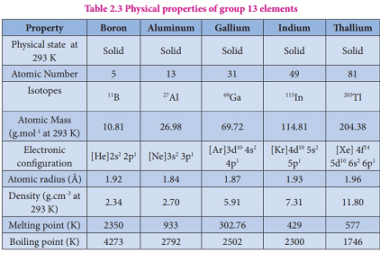
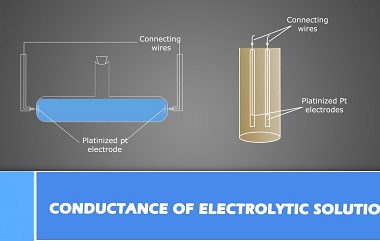
Group 13 Orthoboric acid
Orthoboric acid, also known as boracic acid or H3BO3, is a white, crystalline, weak acid that belongs to Group 13 of the periodic table. It is composed of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms, with a chemical formula of H3BO3. Orthoboric acid is commonly used in the production of boron compounds, as a mild antiseptic, and…