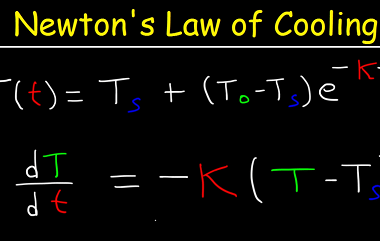
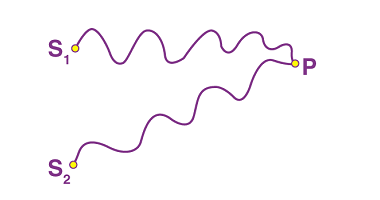
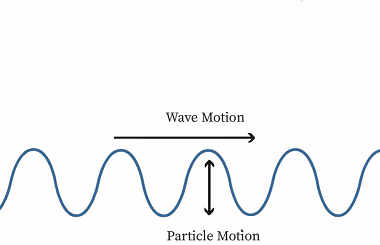
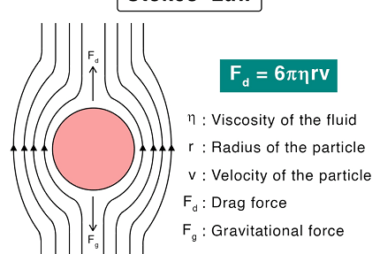
Newton’s law of cooling
Newton’s law of cooling states that the rate of heat loss of a body is proportional to the difference in temperatures between the body and its surroundings. Mathematically, it can be expressed as: dQ/dt = -kA(T – Ts) where: This law is applicable when the temperature difference between the body and its surroundings is not…