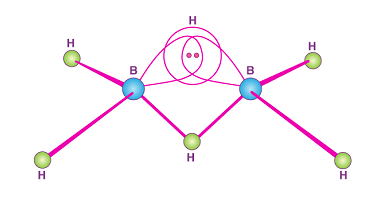
Group 14 Reactivity towards water and halogen
Group 14 of the periodic table includes the elements carbon (C), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), tin (Sn), and lead (Pb). Reactivity towards water: Carbon and silicon do not react with water. Germanium reacts with water to form germanium dioxide (GeO2) and hydrogen gas (H2). Tin reacts slowly with water to form tin(II) oxide (SnO) and…