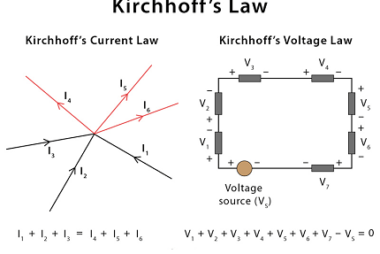
Kirchhoff’s law
Kirchhoff’s laws refer to two fundamental laws of circuit theory that govern the behavior of electrical circuits. These laws are essential tools in circuit analysis and can be used to solve complex electrical circuits with multiple components and sources. What is Required Kirchhoff’s law Kirchhoff’s laws are fundamental laws of circuit theory and are required…