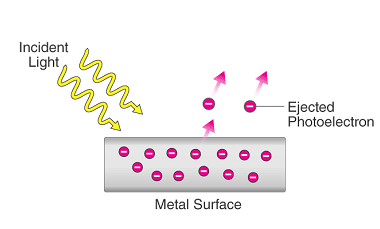
Photoelectric Effect
The photoelectric effect is the phenomenon of the emission of electrons from a material when it is exposed to electromagnetic radiation, such as visible light or ultraviolet light. This effect was first observed by Heinrich Hertz in 1887 and was explained by Albert Einstein in 1905, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics…