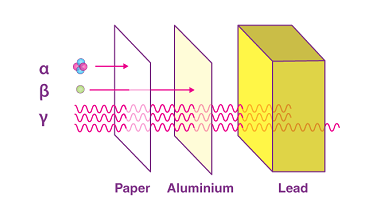
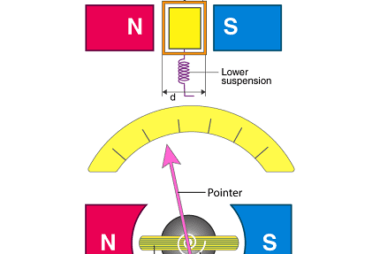
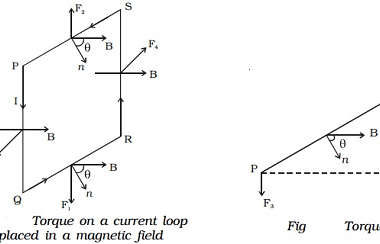
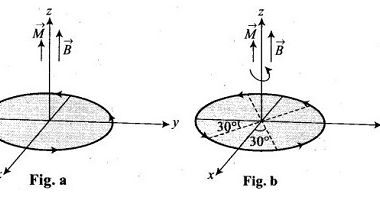
Refraction at plane
Refraction at a plane occurs when a light wave passes through an interface between two materials with different refractive indices. When this happens, the direction of the light wave changes, and the wave bends either towards or away from the normal, which is an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface of the interface. The amount…