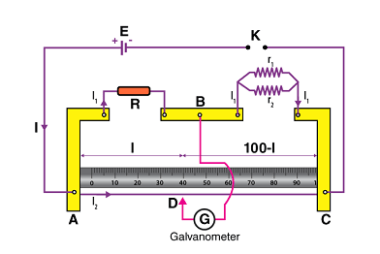
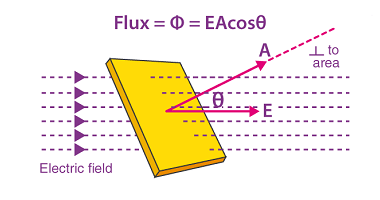
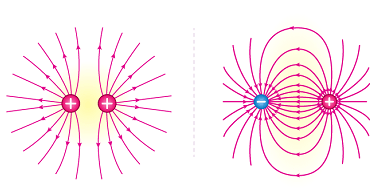
Parallel arrangements of resistances
When resistors are arranged in parallel, they are connected in such a way that the same voltage is applied across each resistor, and the current is divided among the resistors. The total resistance of the parallel circuit is less than the value of the smallest resistor in the circuit. The current flowing through each resistor…