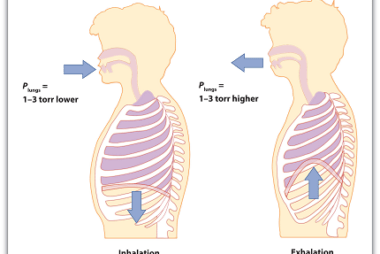
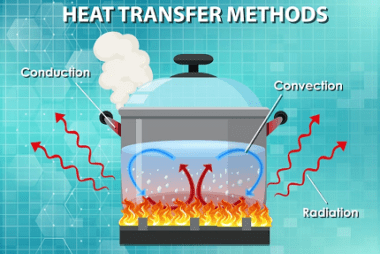
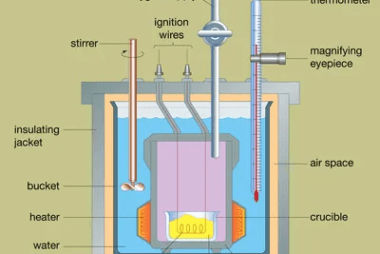
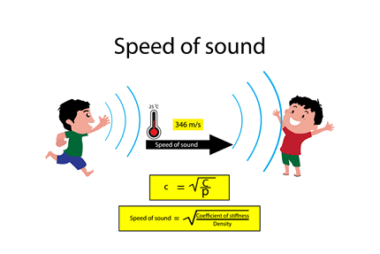
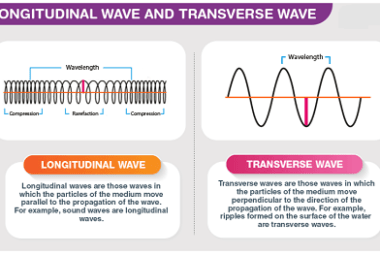
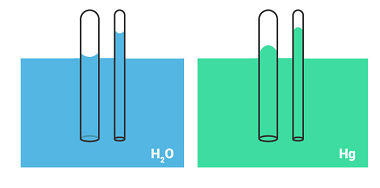
Irreversible processes
Irreversible processes are processes that cannot be reversed, either naturally or artificially. In thermodynamics, an irreversible process is one in which the total entropy of the system and its surroundings increases. This increase in entropy results in a loss of useful energy, and the process cannot be reversed to return the system to its original…