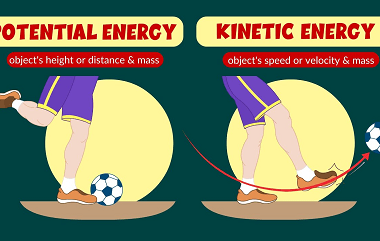
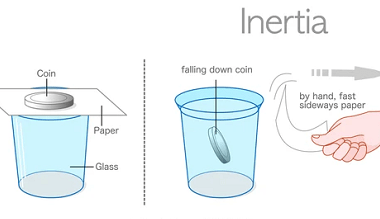
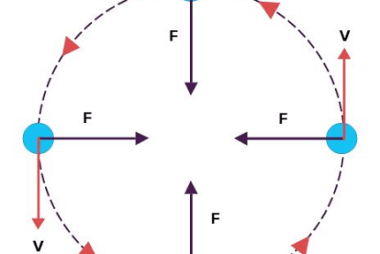
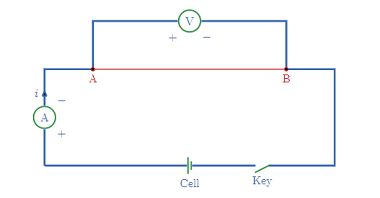
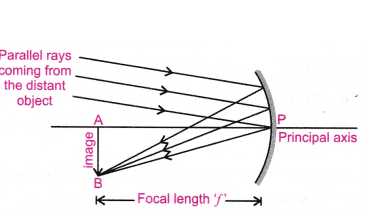
Its motion
Motion refers to a change in an object’s position with respect to its surroundings over time. It is commonly described in terms of displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Displacement is the change in position of an object from its initial position to its final position, while velocity is the rate at which an object changes its…