Advance Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Ampere’s Law
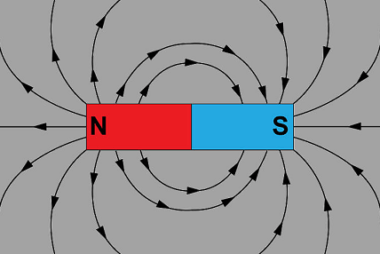
Ampere’s Law Ampere’s Law is a fundamental principle in electromagnetism that relates the magnetic field to the electric current flowing through a closed loop. It was formulated by the French physicist André-Marie Ampère. Ampere’s Law states that the line integral of the magnetic field, denoted as B, around a closed path, known as an Amperian…