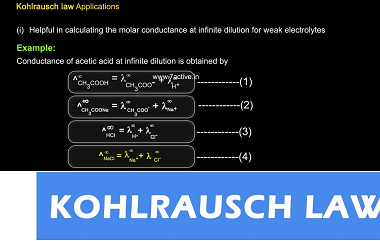
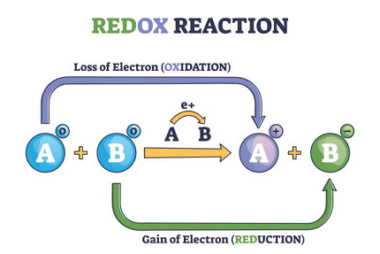
Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Electrolysis
Electrolysis Electrolysis is a chemical process that involves the use of an electric current to induce a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. It is a technique used to decompose compounds into their constituent elements or ions by passing an electric current through an electrolyte. In electrolysis, an electrolyte is a substance, either in a molten state or…