Advance Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Laws of Electrolysis
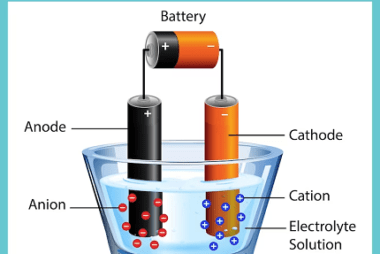
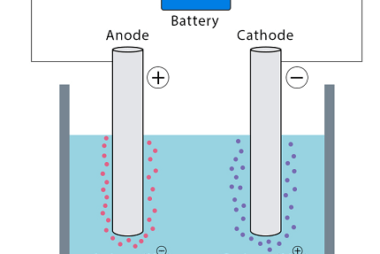
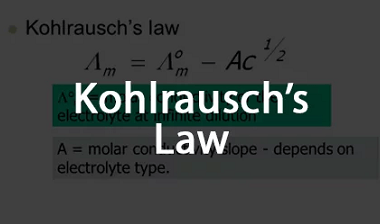
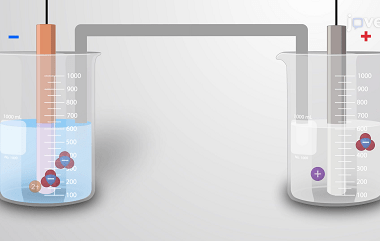
Laws of Electrolysis The Laws of Electrolysis are a set of principles formulated by Michael Faraday that describe the quantitative relationships between the amounts of substances involved in an electrolytic reaction. These laws are: These laws provide a basis for understanding and quantifying the electrolytic processes, such as the deposition of metals during electroplating or…