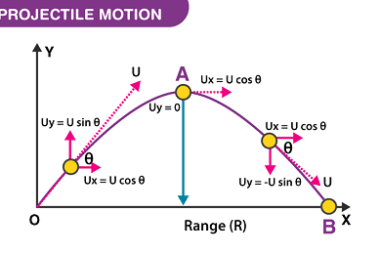
Impulse
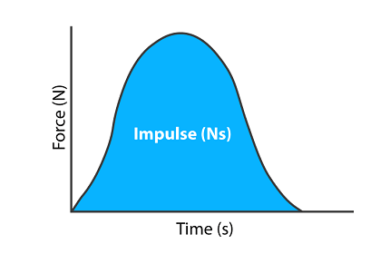
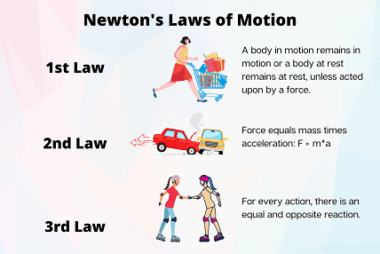
In physics, an impulse is defined as the change in momentum of an object over a period of time. It is given by the product of force and the duration of the force applied. Mathematically, it is expressed as: Impulse = Force × Time The impulse is a vector quantity, and its direction is the…