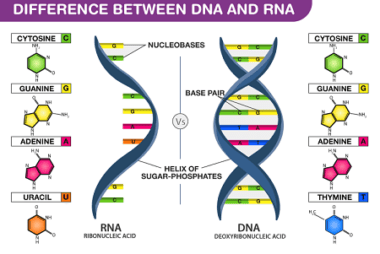
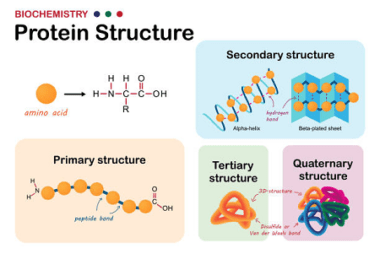
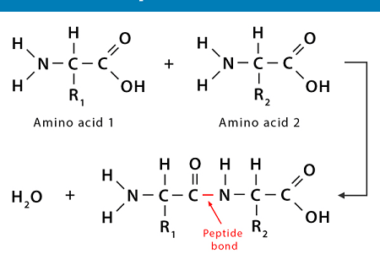
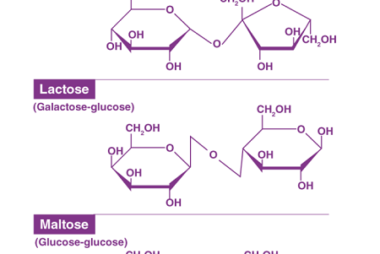
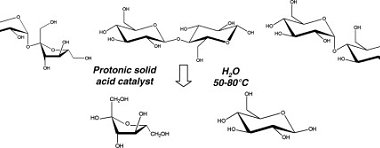
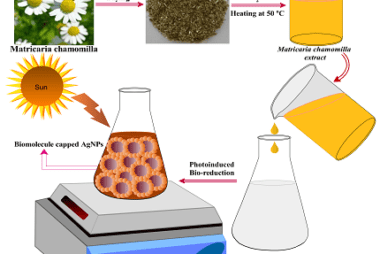
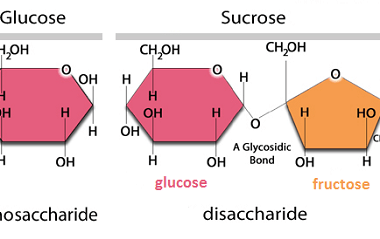
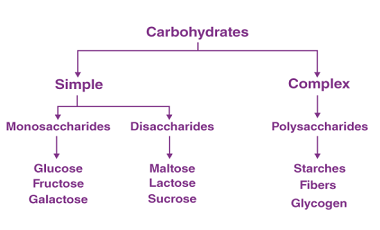
Structure of DNA and RNA
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) are the two types of nucleic acids that are found in all living organisms. They play a critical role in storing, transmitting, and expressing genetic information. The structure of DNA is a double helix, consisting of two complementary strands of nucleotides. A nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous…