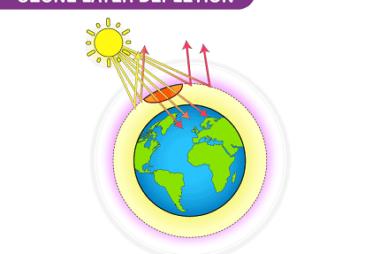
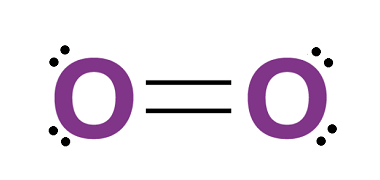
Group 18 Chemical properties and uses
Group 18 of the periodic table, also known as the noble gases, includes helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn). These elements are all chemically stable and have a complete outermost shell of electrons, making them very unreactive. Here are some of the chemical properties and uses of these…