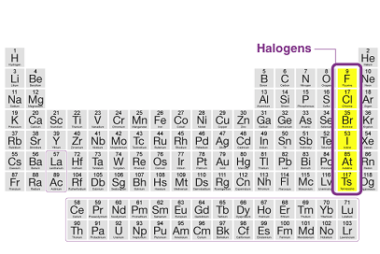
Group 13 Alkalis
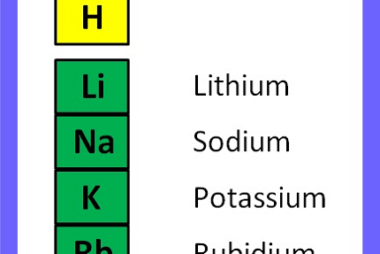
I believe you might be referring to Group 1A (also known as Group 1 or the alkali metals) on the periodic table of elements. This group includes the following elements: These elements are all highly reactive metals with low melting and boiling points. They are called “alkali” metals because they react with water to form…