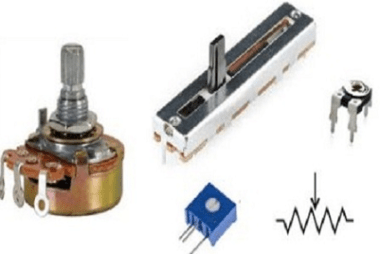
Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Potentiometer – concepts and applications
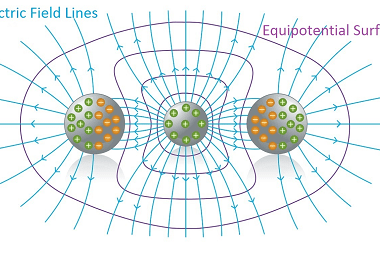
Potentiometer – concepts and applications Certainly! Here’s a detailed explanation of the concepts and applications of a potentiometer: Concepts: Applications: These are some of the key concepts and applications of a potentiometer. The specific depth and extent of these topics may vary depending on the level of study and the course requirements. The Physics syllabus…