Advance Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Amorphous
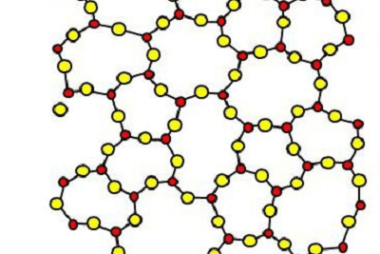
Amorphous Amorphous refers to a state or structure lacking a regular, ordered arrangement of atoms or molecules. Unlike crystalline materials, which have a well-defined, repeating pattern, amorphous materials exhibit a more random or disordered atomic arrangement. Amorphous substances can exist in various forms, such as amorphous solids or amorphous liquids. Some common examples of amorphous…