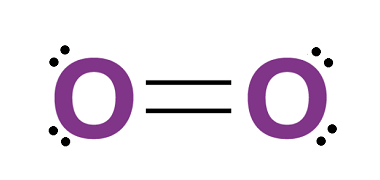
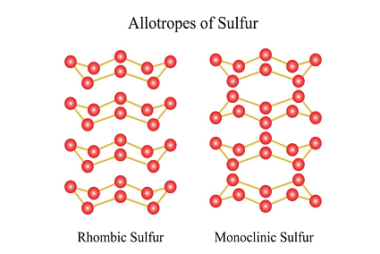
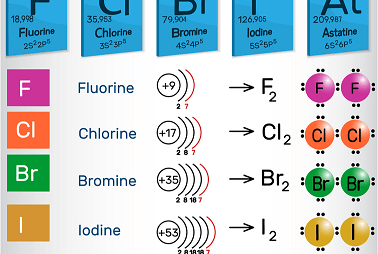
Group 16 Uses of dioxygen
Dioxygen, also known as molecular oxygen or simply oxygen, is a gas that makes up about 21% of Earth’s atmosphere. It is an essential element for life as we know it, and has many important uses in various fields. Here are some of the uses of dioxygen: Overall, dioxygen is an incredibly versatile element that…