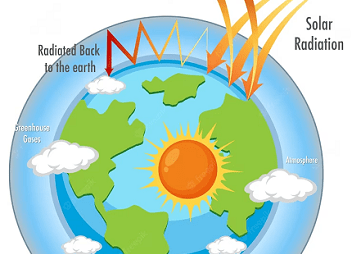
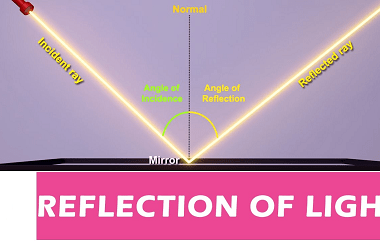
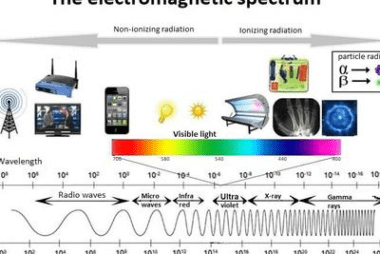
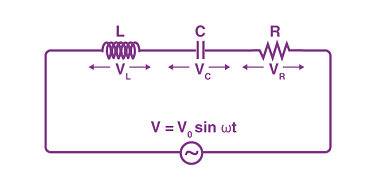
Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Einstein’s photoelectric equation
Einstein’s photoelectric equation Einstein’s photoelectric equation, also known as the photoelectric effect equation, describes the relationship between the energy of a photon and the maximum kinetic energy of an emitted electron during the photoelectric effect. The equation is as follows: E = hf – φ Where: The photoelectric effect is the phenomenon where electrons are…