Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Mutual Inductance
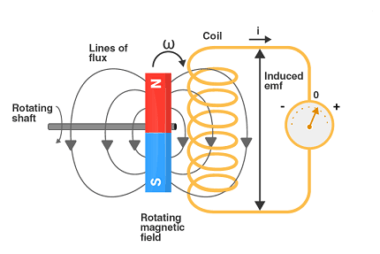
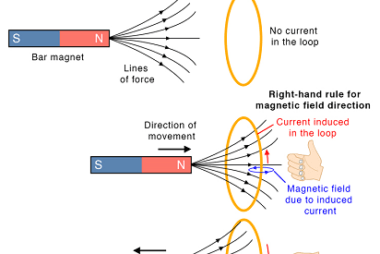
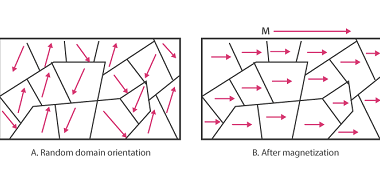
Mutual Inductance Mutual inductance is a fundamental concept in electromagnetism that describes the relationship between two adjacent conductors or coils. It is defined as the ability of one coil to induce an electromotive force (EMF) or voltage in the other coil when the current flowing through the first coil changes. Here are some key points…