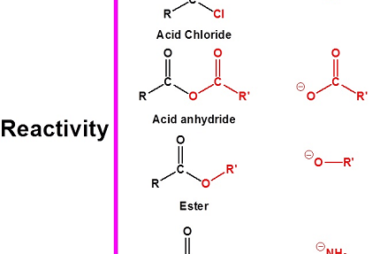
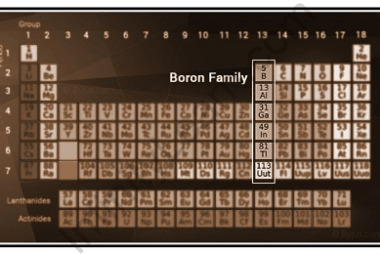
Group 13 Reactivity towards acids
Group 13 elements in the periodic table include boron (B), aluminum (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In), and thallium (Tl). In general, the reactivity of Group 13 elements towards acids increases down the group. Boron, being the least reactive element in the group, does not react with acids at room temperature. Aluminum, gallium, indium, and thallium…