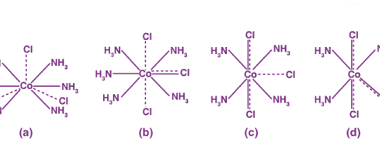
Werner’s theory
There are several theories associated with the name “Werner,” so it’s important to specify which one you’re referring to. However, I’m assuming that you’re referring to the “Werner’s Theory of Coordination Compounds” proposed by Alfred Werner. Alfred Werner was a Swiss chemist who developed the theory of coordination compounds in the early 1900s. According to…