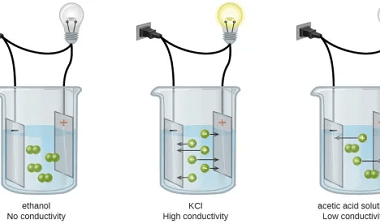
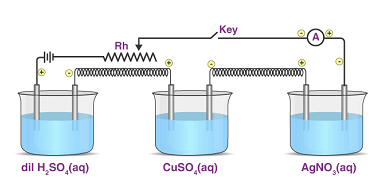
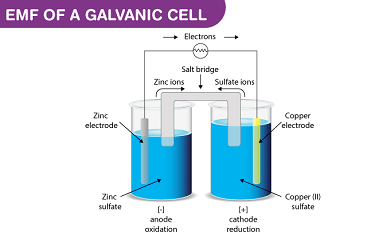
Oxidation states
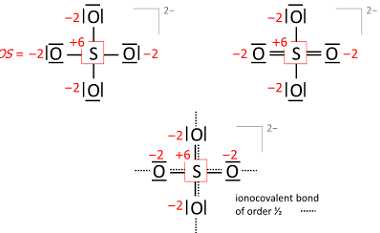
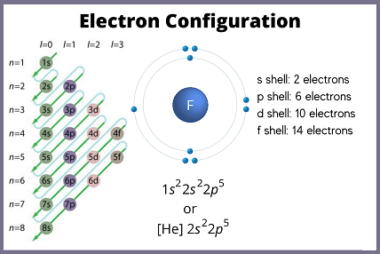
Oxidation state is a measure of the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. It is represented by a positive or negative number, called the oxidation number, which reflects the number of electrons an atom has gained, lost or shared in forming a chemical bond with another atom. The oxidation state of…