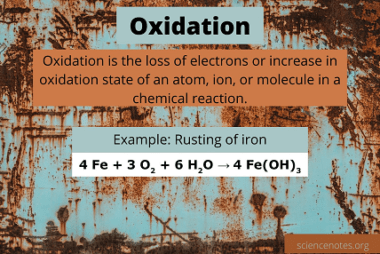
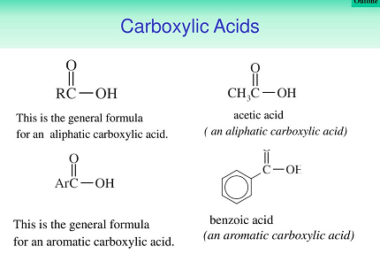
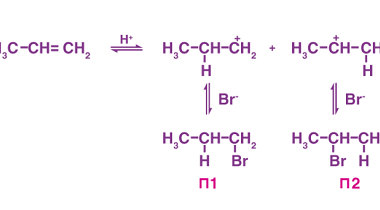
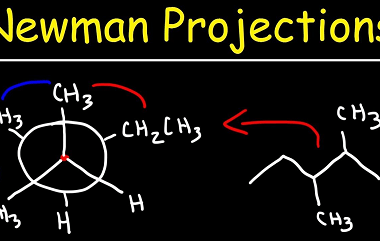
Oxidation
Oxidation is a chemical process in which a substance loses electrons. It is often defined as the process in which a substance reacts with oxygen to form an oxide. Oxidation reactions can also involve other elements, such as hydrogen or chlorine, and can occur without the presence of oxygen. In an oxidation reaction, the substance…